If you feel this doesn’t help you obtain a higher grade, simply email me within 7 days of purchase and I will grant a full refund.
Org 1 Summary Sheets
The 20-page summary that should have come with your textbook. Show more
- These sheets provide a condensed summary of an entire Org 1 course, so you can access the key concepts, reactions, and mechanisms from your textbook in just a few pages.
- If your midterm or final is fast approaching, and you feel behind in your exam prep these notes can help you get up to speed - fast!
- Designed for introductory organic chemistry courses at all levels in the USA and Canada (including ACS exams), but also useful as a refresher on the basics!
-
Immediate download for test prep -
Print ready PDF - nothing is mailed -
Contains key concepts covered in exams
What's inside
Showing 4 of 12See All
Page 1 of 12

1. Bonding & Hybridization
What is bonding and why does it occur – What is antibonding – What is pi bonding –Hybridization – sp3 sp2 and sp hybridization examples – Trigonal pyramidal, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, linear, bent geometries – How does hybridization affect bond strength – Shortcut for finding hybridization of any atom

2. Formal Charge, Dipoles, Boiling Points, and Curved Arrows
How to calculate the formal charge of an atom – Identifying dipoles – Dipoles are the key to understanding boiling points and reactivity – Dipole moments Factors that affect boiling points - –Four key forces – Ionic , hydrogen bonding, van der Waals dipole and dispersion interactions – Curved arrows and how to use them – Three legal moves for curved arrows – Examples of curved arrows

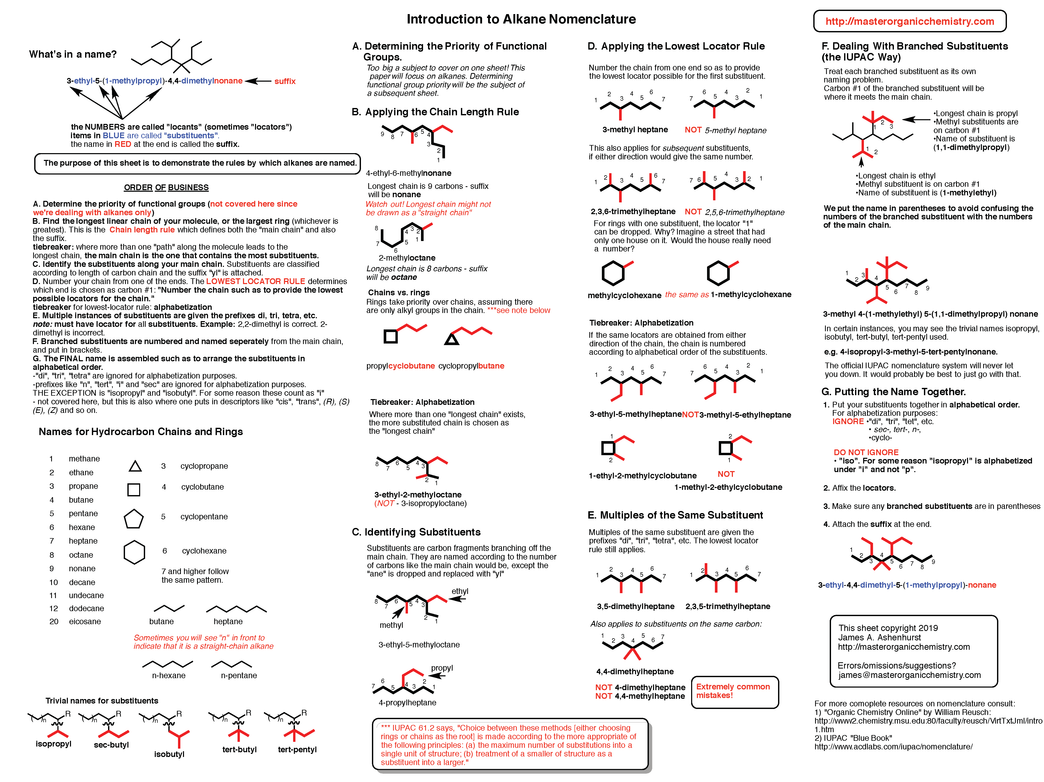
3. Introduction to Alkane Nomenclature
How to name organic compounds - Functional group priorities - Applying the chain length rule – Identifying substituents – The lowest locator rule – Dealing with multiple and branched substituents – Putting it all together

4. Conformations and Newman Projections
What are conformations – The Newman projection – Staggered and eclipsed – Identifying syn, anti, gauche interactions – Calculating energies of conformations using a “price list” – Mapping out conformation energies on a graph
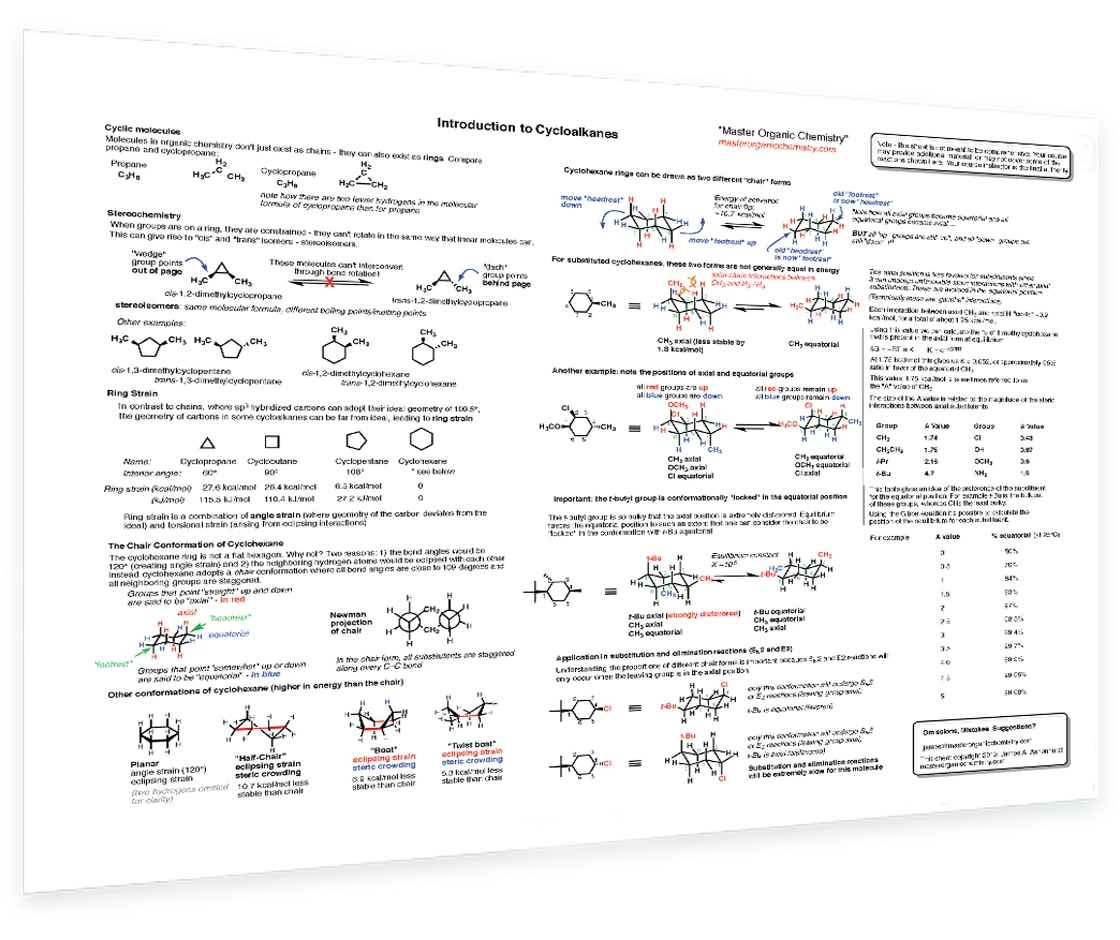
5. Cycloalkanes
Examples of cyclic alkanes – Geometric isomers - cis and trans – Ring strain of cyclopropane and cyclobutane – Chair conformation of cyclohexane – Drawing Newman projection of a chair – How to do a chair flip – Equatorial and axial positions – A values – Calculating relative different energies of conformations – Application in substitution and elimination reactions

6. Resonance
What is resonance – Resonance hybrids – How to use curved arrows to interconvert resonance forms – 5 steps to figuring out the most stable resonance form – Applying resonance to understand reactions – pi donors and pi acceptors
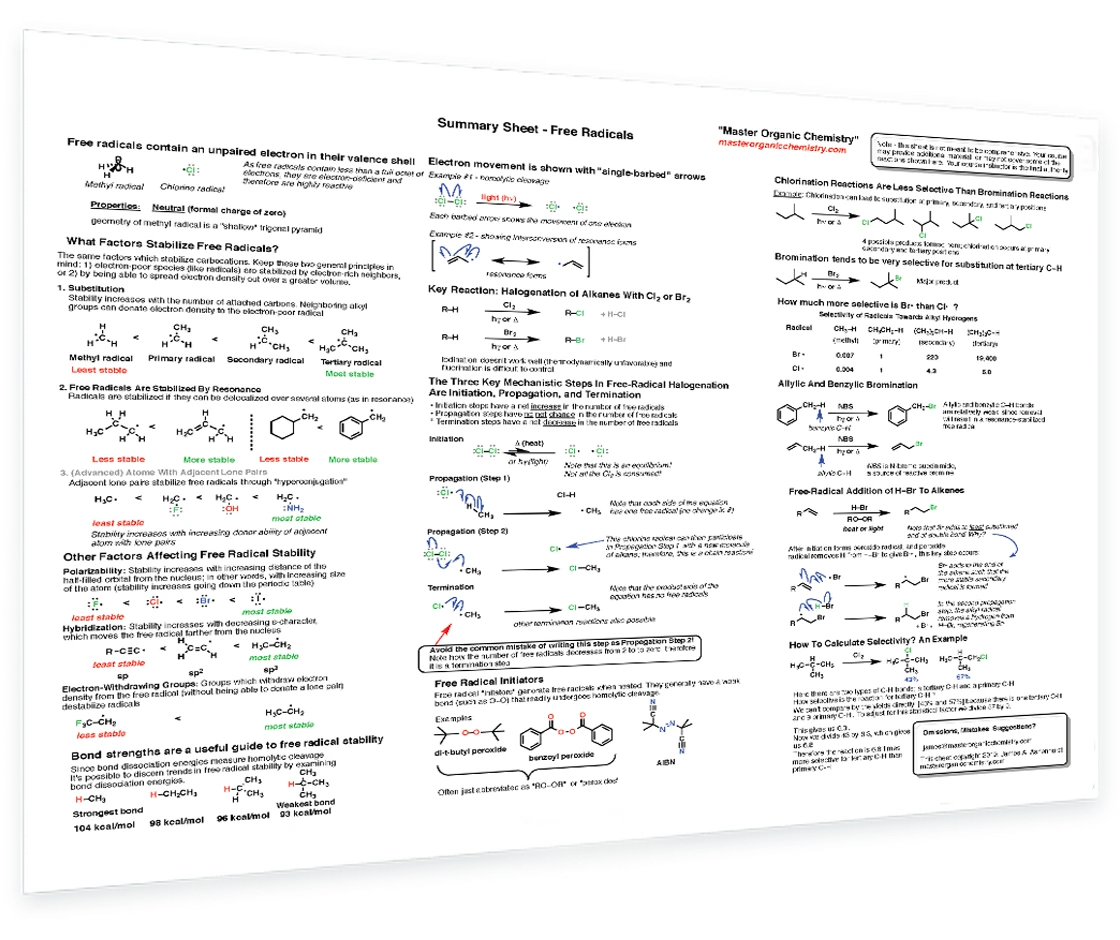
7. Free Radicals
What is a free radical? – 3 key factors that stabilize free radicals –Bond strengths as a guide to radical stability – Showing electron movement with single barbed arrows – Halogenation of alkanes – Recognizing initiation, propagation, termination steps – Identifying free radical initiators – Selectivity of bromine vs chlorine – Allylic and benzyilic bromination – Free radical addition of hbr to alkenes – Calculating selectivity

8. Introductions to Acids & Bases
Introduction to acids and bases – Bronsted and Lewis definitions of acids – Simple examples of acid base reactions - The four key actors – How to define and measure acidity – Ka and pKa – 6 key factors that affect acidity - Charge, electronegativity, polarizability, resonance, inductive effects, hybridization – How to tell if an acid base reaction will be favorable or not using pKa

9. Substitution & Elimination
The SN2 mechanism - Steric effects - Polar aprotic solvents and the SN2 - What makes a good leaving group - How the substrate influences reactivity - 4 key factors that affect nucleophilicity - Good, OK and weak nucleophles – The e2 mechanism - strong bases - periodic trends for basicity
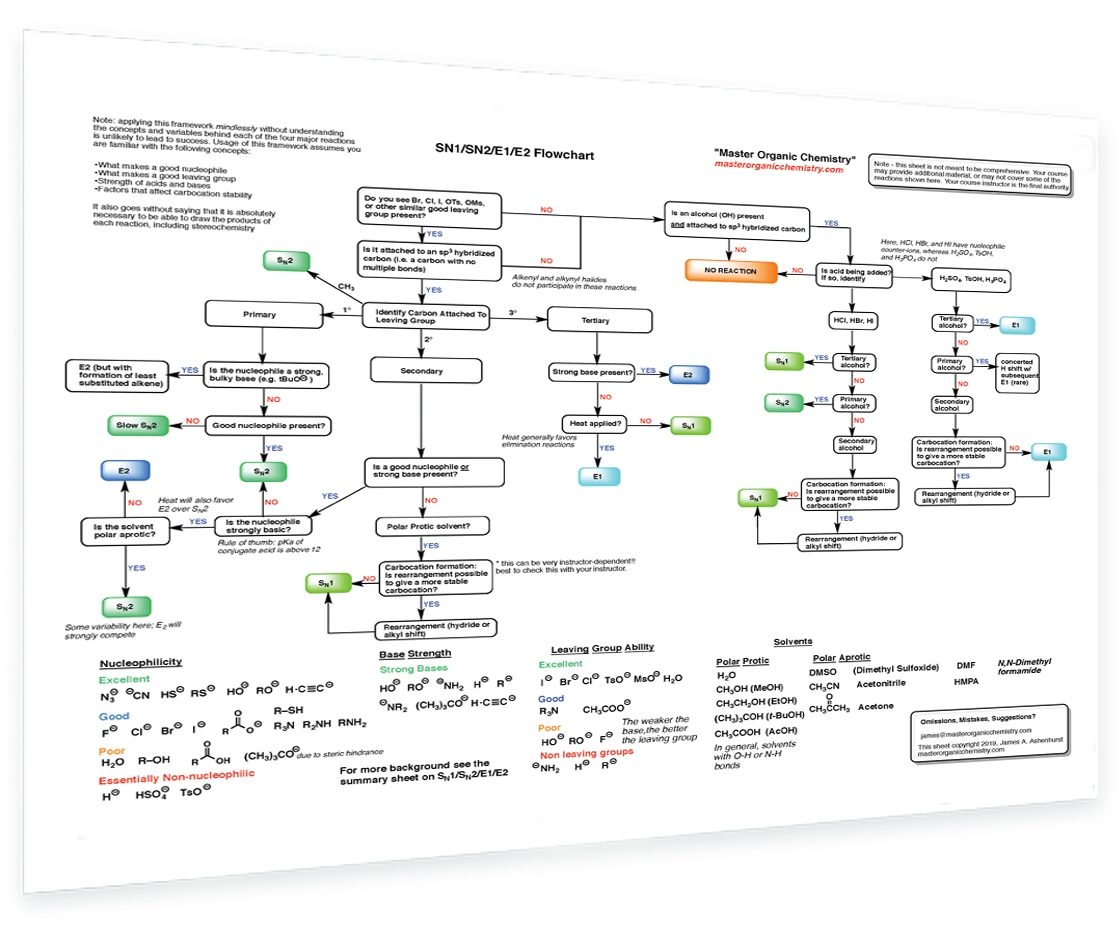
10. SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Decision
How to determine if a reaction will proceed via SN1, SN2, E1 or E2? This handy flowchart covers all the possibilities and will help you make the right decision.

11. Alkene Reactions
All the key reactions of alkenes on a single page, with notes on their stereochemistry, Markovnikov's rule, possible rearrangements, and more.

12. Alkyne Reactions
Key reactions of alkynes - the reagents, bonds formed/broken, stereochemistry, and more.
Your purchase is safe
- James Ashenhurst, Owner